What is the variance analysis cycle?
The variance analysis cycle is a systematic process of comparing actual financial performance against planned or standard performance. It helps us understand the "why" behind the "what" when it comes to deviations between our financial plans and actual results.
Think of it like this: you've carefully crafted a budget for your project, estimating costs for materials, labor, and overhead. But, midway through the project, your expenses are exceeding projections. 🚀
The variance analysis cycle is like figuring out why these costs are off (maybe material prices rose unexpectedly, productivity levels were lower than anticipated, or there were unforeseen changes).
This cycle helps us unravel the reasons behind the differences between what we expected to happen financially (budgeted or planned figures) and what actually happened (our real-world results).
By understanding these variances, we can:
- Identify areas for improvement: Is there a cost overrun because of inefficiencies, or did unforeseen circumstances impact sales?
- Make smarter decisions: Knowing the "why" behind variances helps us make informed choices about resource and budget allocation and future plans.
- Boost overall performance: By analyzing variances, we can continuously refine our forecasting and planning processes, leading to better financial health.
What are the steps in the variance analysis cycle?
The variance analysis cycle is a framework for understanding why your financial results might differ from what you originally planned.
Here are the key steps to follow:
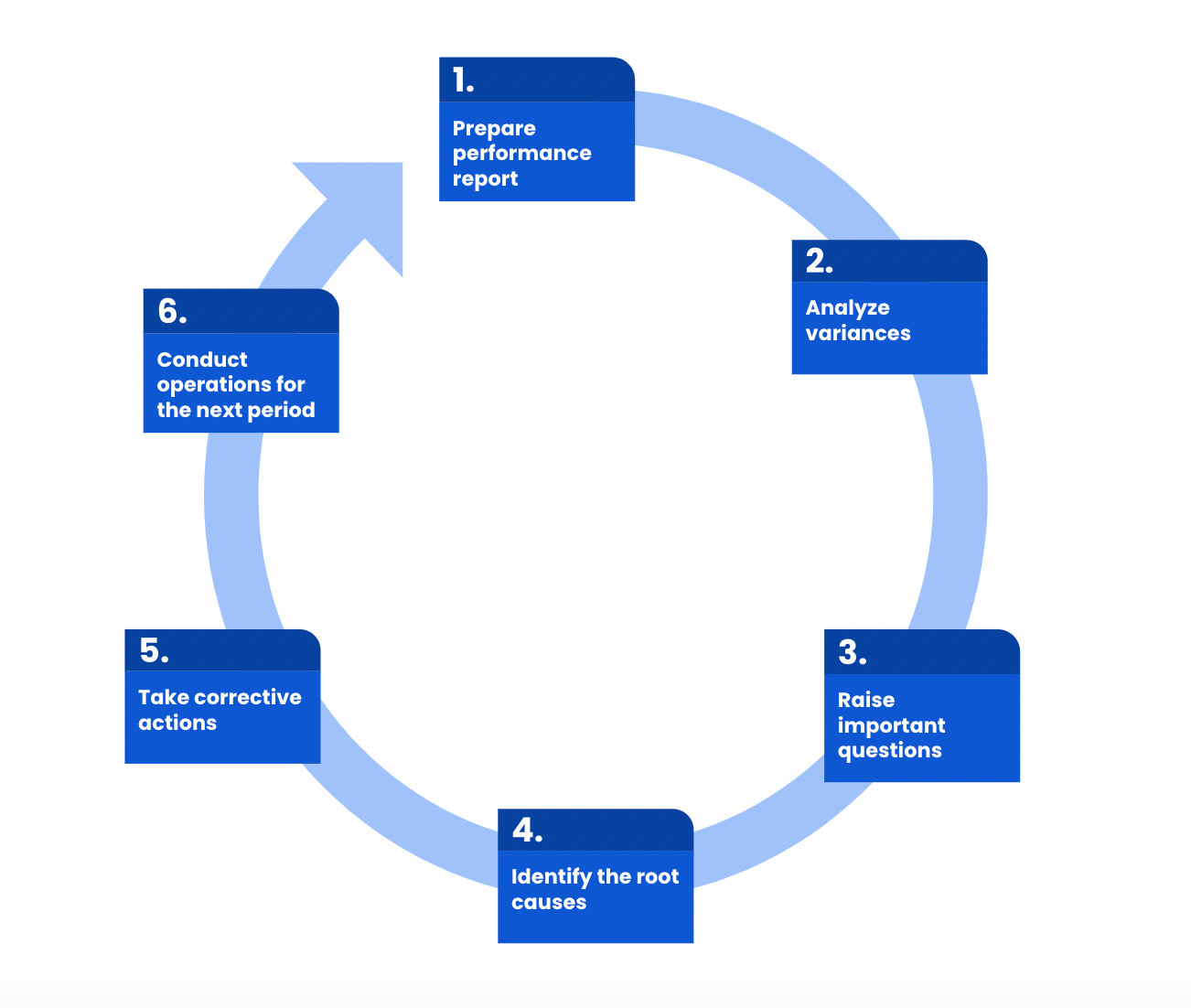
1. Prepare performance report
Document everything in a clear performance report. This includes:
- Any variances you found
- Why you think they happened
- What steps you took to address them
- The results of those actions
By doing this, you'll create a baseline for identifying and quantifying any variances. Your performance report serves as valuable documentation and helps guide future decision-making.
2. Analyze variances
Once the performance report is prepared, the differences between the actual results and budgeted values are calculated. This analysis helps identify potential areas of concern and efficiency.
3. Raise important questions
Next, compare your budget or forecasts to your actual results. Where do you see differences?
Don't just note the numbers, start asking questions:
- Why are our expenses higher than we thought?
- Did something cause our sales to fall short?
- Are there unexpected factors dragging down our profits?
4. Identify the causes
Once you have a list of questions, it's time to dig deeper and identify the root causes of the variances. This involves gathering data, analyzing trends, and conducting various 'investigations'.🕵🏼♂️
You might need to:
- Review historical data to identify patterns and trends.
- Consult with operational teams to understand specific challenges and inefficiencies.
- Analyze market data to identify external factors influencing performance.
5. Take corrective actions
Based on your findings, it's crucial to take action to address the identified variances. Possible actions resulting from the variance analysis cycle may involve:
- Implementing corrective measures to improve efficiency, reduce costs, or boost sales.
- Reallocating resources to capitalize on opportunities or mitigate risks.
- Revising budgets and forecasts to reflect new realities and insights.
6. Conduct operations for the next period
By the time you’ve reached this step, you’ve got enough knowledge to tackle the next period’s operations with a more informed approach.
Think about applying what you learned to help set more achievable targets, allocate resources better, and implement proactive measures to prevent future variances.

Why do variances occur?
Variances occur because reality doesn't always perfectly match our plans. These discrepancies can arise from various factors, both internal and external to the company.
Here are some of the most common reasons for variances:
- Market fluctuations: Unexpected changes in the market, like sudden increases in raw material prices or dips in consumer demand, can throw your budget off track.
- Operational inefficiencies: Internal factors like production delays, excessive scrap, or inefficiencies in resource allocation can lead to higher costs or lower output than anticipated.
- Pricing issues: Unforeseen changes in competitor pricing strategies or an inability to raise your prices as planned can impact your revenue stream negatively.
- External factors: Unexpected events like natural disasters, political instability, or changes in regulations can disrupt your operations and financial performance.
- Human error: Mistakes in planning, budgeting, or execution can also lead to variances.
The formula behind the analysis
The variance analysis cycle relies on a specific formula to quantify the difference between budgeted and actual results.
Let's break down the formula itself, how to use it in Excel, and explore specific variations…
What is the formula for variance analysis?
The core formula for variance analysis calculates the difference between the budgeted (or planned) value (B) and the actual value (A):
Variance = Actual (A) - Budgeted (B)
This straightforward formula provides a basic understanding of how much your results deviated from your expectations.
However, for a deeper analysis, we need to consider different types of variances, leading to more specific formulas.
What is the formula for variance analysis in Excel?
Excel offers various built-in functions to calculate variances depending on what you're analyzing and whether you're dealing with the entire population or a sample:
Population variance: Use the VAR.P(range) function, where "range" refers to the cells containing your data.
Sample variance: Use the VAR.S(range) function.
Price variance: This calculates the difference between the actual price paid (AP) and the budgeted price (BP) multiplied by the actual quantity (Q):
Price Variance = (AP - BP) * Q
Quantity variance: This calculates the difference between the actual quantity (Q) and the budgeted quantity (BQ) multiplied by the budgeted price (BP):
Quantity Variance = (Q - BQ) * BP

How do you use the variance formula?
Here's a general step-by-step approach to using the variance analysis cycle formula in Excel:
1. Input your data: Enter your budgeted and actual values in separate columns.
2. Choose the appropriate formula: Depending on the type of variance you're analyzing (population, sample, price, or quantity), select the appropriate formula from the above options.
3. Reference your data: Enter the cell range containing your budgeted and actual values into the formula function.
4. Calculate the variance: Press Enter to calculate the variance for each data point.
5. Analyze the results: Look for significant variances and use them as a starting point for further investigation into the root causes.
By understanding the basic formula and its variations in Excel, you can unlock valuable insights from your financial data and utilize the variance analysis cycle effectively to enhance your financial planning and decision-making.
Types of variance analysis
The variance analysis cycle dives deeper by focusing on specific areas within your budget. This lets you pinpoint the root causes of variances much better.
Below, we'll explore three common types of variance analysis: material, labor, and overhead variances.
1. Material variance analysis
This focuses on understanding the difference between the actual cost of materials used (ACM) and the budgeted cost of materials (BCM) for the actual quantity (Q) used:
Material Variance = (ACM - BCM) * Q
This variance can be further broken down into price variance (difference between actual and budgeted price per unit) and quantity variance (difference between actual and budgeted quantity used).
2. Labor variance analysis
This examines the difference between the actual cost of labor (ACL) and the budgeted cost of labor (BCL) for the actual hours worked (AH):
Labor Variance = (ACL - BCL) * AH
Like material variance, this can be further analyzed as labor rate variance (difference between actual and budgeted hourly wage) and labor efficiency variance (difference between actual and budgeted hours worked for a given output).
3. Overhead variance analysis
This analyzes the difference between the actual overhead cost (AOC) and the budgeted overhead cost (BOC):
Overhead Variance = (AOC - BOC)
Overhead costs are indirect and often fixed within a specific time period. Therefore, this variance can be further categorized as fixed overhead spending variance (difference between actual and budgeted fixed overhead cost) and variable overhead spending variance (difference between actual and budgeted variable overhead cost per unit of activity).

How to calculate spending variance
Spending variance refers to the difference between the actual amount you spent and the amount you budgeted to spend.
To calculate spending variance, you can use this formula:
Spending Variance = Actual Spending - Budgeted Spending
Let's say you planned to spend $500 on marketing for the month. However, due to unforeseen circumstances, your actual spending reached $620. Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
Spending Variance = $620 (Actual) - $500 (Budgeted) = $120
In this case, the positive variance of $120 indicates that you overshot your budget by $120. This could be a cause for concern, prompting you to investigate further and take corrective actions.
Remember, variances can be favorable or unfavorable depending on the situation and your goals. By calculating and understanding spending variances, you gain valuable insights into your spending patterns and can make informed decisions to optimize your financial health.
What is budget variance analysis?
Budget variance analysis compares actual results to the original budget. It's a broader approach that doesn't necessarily consider standard costs and can be used for various expense categories, including materials, labor, and overheads.
What is the standard cost variance analysis?
Standard cost variance analysis compares actual results to predefined standard costs. Standard costs are predetermined estimates of what a cost should be under normal operating conditions.
This approach allows for a more detailed understanding of cost variances beyond simply comparing actuals to the budget.

Is variance positive or negative?
Variance itself isn't inherently positive or negative. It's simply the difference between what you expected (budgeted) and what actually happened. It's like the gap between your planned destination and the actual road you end up taking.
However, the context of the variance matters more:
If the actual cost comes in under budget (positive variance), that's a good thing.
But, if the actual cost is higher than expected (negative variance), that means you went over budget. This might not be ideal, but it helps you understand where you might need to adjust your spending in the future.
So, while the variance itself doesn't have a positive or negative sign, understanding the "why" behind the variance helps you determine if it's an opportunity to celebrate or a cause for further analysis and potential adjustments.
Can variance be zero?
Yes, a variance can be zero! This occurs when the actual results perfectly match the budgeted or planned figures.
In simpler terms, it means everything went exactly according to plan, with no surprises (either positive or negative) in terms of costs, revenues, or other financial metrics.
What causes an unfavorable variance?
Not all variances are created equal. While some might be cause for celebration (think coming in under budget), others can raise an eyebrow or two.
Unfavorable variances occur when the actual results fall short of expectations, meaning your expenses are higher or your revenues are lower than what you budgeted for.
So, what leads to unfavorable variances?
Some common culprits include:
- Market fluctuations: Unexpected changes in the market, like a sudden rise in raw material prices or a dip in consumer demand, can throw your budget off track.
- Operational inefficiencies: Internal factors like production delays, excessive scrap, or inefficiencies in resource allocation can lead to higher costs or lower output than anticipated.
- Pricing issues: Unforeseen changes in competitor pricing strategies or an inability to raise your own prices as planned can impact your revenue stream negatively.
- External factors: Unexpected events like natural disasters, political instability, or changes in regulations can disrupt your operations and financial performance.
These are just a few examples, and the specific causes of unfavorable variances will vary depending on your industry and unique circumstances.
Are unfavorable variances always bad?
While unfavorable variances, meaning actual results falling short of expectations, are generally unwelcome surprises, they're not always a bad thing.
If you want to have a more positive outlook on things, you can look at them as valuable wake-up calls, prompting deeper analysis of inefficiencies and corrective actions that ultimately lead to improved performance and future cost-saving opportunities.
The key is to view them not as failures, but as stepping stones toward ongoing financial optimization.
How to tell if variance is favorable or unfavorable
Imagine you budgeted to spend $100 on office supplies for the month, but only ended up spending $83. Great news, right? This favorable variance means you spent $17 less than expected, saving some precious cash.
However, the opposite scenario can also occur. If you budgeted $100 but ended up spending $123, you have an unfavorable variance. This means you overshot your budget by $23, a potential cause for concern.
Here's how you can tell if the variance is favorable or unfavorable:
- Favorable variance: Actual results are better than the budget (e.g., spending less than expected).
- Unfavorable variance: Actual results are worse than the budget (e.g., spending more than expected).

How often is variance analysis performed?
The frequency of variance analysis can vary depending on several factors, but some typical timeframes and influencing elements are worth exploring.
Some common frequencies include monthly, quarterly, or biannually (twice a year).
Let’s take a closer look at why some finance and FP&A teams choose these timeframes:
Monthly
This is a popular choice for many companies because it enables timely identification and response to variances before they snowball into bigger issues. It provides a good balance between capturing recent trends and maintaining a manageable workload for FP&A teams.
Quarterly
This approach offers a broader perspective, enabling analysis of longer-term trends and potential seasonal fluctuations. It might be suitable for companies with more stable operations or less volatile industries.
Biannually
This is less frequent but can be appropriate for businesses with highly predictable and stable financial performance or those with limited resources for frequent analysis.
There's no one-size-fits-all answer to how often variance analysis should be performed. And it’s important to keep in mind that frequency can vary based on:
- Industry volatility (e.g., tech vs. utilities)
- Company size and complexity (larger = more frequent)
- Risk tolerance and management style (conservative = more frequent)
- Significance of variances (major variances = more frequent)
- Available FP&A resources (limited resources = less frequent)
How to write a variance analysis report
Variance analysis reports are important for understanding why your financial results might differ from your plans. But how do you write a report that's clear, informative, and engaging?
Here are some tips to help you write a variance analysis report:
Structure:
1. Start with a strong introduction: Briefly introduce the report, stating the period analyzed and the key variances investigated.
2. Findings (show, don’t just tell): Present the identified variances in a clear and concise format, like tables or charts. Include explanations for each significant variance, using clear and non-technical language.
3. Analysis: Dig deeper into the "why" behind the variances. Explain the root causes, using data, examples, or insights from discussions with relevant teams.
4. Action plan: Based on your analysis, propose specific actions to address the variances. This might involve cost-saving measures, pricing adjustments, or process improvements. Be clear about who is responsible for implementing each action item.
5. Wrap it up: Summarize your key findings and reiterate the impact of the variances on the organization's financial performance. Briefly mention any recommendations for future planning or process improvement.
Key components:
- Clarity is king: Use simple language, avoid technical terms, and explain any necessary jargon.
- Visual appeal: Use charts, graphs, or tables to present complex data efficiently and visually.
- Actionable insights: Don't just present the problems; provide concrete solutions and recommendations.
- Keep it concise: Aim for a focused report, avoiding unnecessary details or fluff.
By following these tips, you can create a powerful variance analysis report that informs and empowers your colleagues to make data-driven decisions.

FAQs: The variance analysis cycle
What is the variance analysis cycle?
The variance analysis cycle is a continuous process of comparing actual results to planned figures, analyzing the differences (variances), identifying root causes, and taking corrective actions to improve future performance.
How are variances investigated and resolved?
To investigate and resolve variances, you'd gather relevant data, analyze trends, consult with stakeholders from different departments to gain insights, identify the underlying reasons behind the variances, and develop and implement corrective actions like cost-saving measures, pricing adjustments, or process improvements.
What is the root cause of variance analysis?
The root cause of variance analysis isn't about finding blame, but rather about understanding why actual results differ from planned figures. This knowledge helps prevent similar issues and improve financial planning and decision-making.
What is unfavorable variance?
Unfavorable variance occurs when the actual results fall short of expectations compared to the planned figures, such as experiencing higher costs, lower sales, or lower efficiency levels.
Why do we need a variance analysis?
Variance analysis helps us understand why financial results differ from plans, identify areas for improvement within the organization, and make informed decisions about future plans, resource allocation, and adjustments to strategies.
What are the disadvantages of variance analysis?
While time-consuming and requiring skilled personnel to interpret data and take effective actions, variance analysis is crucial because it helps us understand and address the root causes of discrepancies, ultimately leading to better financial performance.
Why do variances occur?
Variances can stem from various factors, both internal (operational inefficiencies) and external (market fluctuations), and even human error.
How can variances be corrected?
Correcting variances depends on the identified root cause, but might involve implementing cost-cutting measures, adjusting pricing strategies, improving internal processes, or revising future plans and budgets.
Finance Alliance Pro Membership
Tired of feeling stagnant in your FP&A career? Take control and unlock your true potential with the Finance Alliance Pro Membership.
This exclusive community is your secret weapon, connecting you with elite finance professionals and equipping you with the cutting-edge tools and resources you need to dominate the field.
Fuel your growth:
- Engage in high-level discussions with peers, sparking innovative ideas and expanding your perspective.
- Sharpen your skills with access to advanced financial analysis tools and expert-curated resources. ️
- Unlock exclusive career opportunities within a network of industry leaders.
Don't just survive your career, thrive in it. Join Finance Alliance Pro Membership today! 🎓



 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn




